PROTECT NONPROFITS SERVING AMERICA:
KEEP NONPROFITS TAX-EXEMPT
Nonprofits are vital to our communities, providing food, medical care, education, and more.
Some lawmakers are looking for ways to raise money and are considering tapping nonprofit resources. If Congress puts these essential community services at risk, nonprofits would be forced to cut programs, turn people away, or close their doors completely to those in need.
VOTERS OVERWHELMINGLY SUPPORT NONPROFITS’
TAX-EXEMPT STATUS
Recent national polling shows that Americans value the role of nonprofits—and expect elected officials to protect their tax-exempt status. As Congress considers tax reform, voters are sending a clear message: protect nonprofits, protect communities.
NONPROFITS
ARE ESSENTIAL
85%
of voters agree nonprofits are important to our country
BAD POLICY,
BAD POLITICS
53%
of voters say they’d be less likely to support a member of Congress who votes to tax nonprofits
VOTERS BACK
TAX-EXEMPTION
82%
support keeping tax-exempt status in place
Nonprofits are purpose-driven, people-powered, and publicly supported.
Voters want to protect them—and expect leaders in Washington to do the same.
Survey research conducted by Cygnal
Sample size of 1,500 voters surveyed from April 16-21, 2025
TAX-EXEMPTION HISTORY
Tax-exempt status is a designation under the tax code for organizations that meet strict rules to stay open about their finances, serve the public, and reinvest in their mission — not to make money for any individual or private group.
Nonprofits are driven by purpose, not profit.

1913
Recognizing the communal benefit derived from nonprofits, the federal government first provided tax exemption for associations and charitable organizations.

1917
Lawmakers enacted a charitable deduction to encourage charitable giving and ensure nonprofits could continue to provide vital community services.

1943
Revenue Act of 1943 introduced the Form 990 as a way to help ensure that nonprofit organizations continue to meet the requirements for tax-exempt status and provide transparency for donors, stakeholders, and the public.

1950
Revenue Act of 1950 established UBIT (Unrelated Business Income Tax) as a way to ensure fair competition between tax-exempt organizations and for-profit businesses.

1954
The Internal Revenue Code consolidated and expanded nonprofit categories under Section 501(c), exempting organizations from federal income tax.

1969
Tax Reform Act of 1969 introduced reforms to the charitable sector, including increased reporting requirements, limitations on political influence, and payout requirements on private foundations.

2006
Pension Protection Act required Section 501(c)(3) organizations to make their Forms 990-T available for public inspection.

NONPROFITS NURTURE THE PUBLIC GOOD
Philanthropy as Civic Duty
American culture has long emphasized the importance of private giving to support the public good.
Balance of Mission and Regulation
The sector has faced ongoing tension between maintaining independence and adhering to regulations ensuring transparency and accountability.
Collaboration with Government
Tax-exempt organizations have often supplemented or partnered with government efforts in education, tourism, healthcare, social services, and standards-setting.
What’s at Stake?
Legislative proposals to tax nonprofits as though they’re profit-maximizing enterprises designed to enrich shareholders would have dangerous consequences for the communities they serve. This approach would significantly reduce access to essential services and critical support for everyday Americans.
Nonprofits
Provide Jobs
In 2022, 501(c)(3) nonprofits accounted for
12.8M
jobs — accounting for 9.9%
of all employment outside
of government.
Americans
Value Nonprofits
Between 2022 and 2023, more than
75.7M
people volunteered at nonprofits, serving an estimated 4.99B hours, valued at $167.2B.
Associations
Enhance Job Skills
Associations support more than
1M
jobs nationwide that serve over 100M Americans.
Who Is at Risk?
Nonprofit organizations play a critical role in delivering services and strengthening communities.
Learn why losing these essential community services is a cost America can’t afford.

Animal Welfare Groups

Without Tax Exemption:
- Overcrowded shelters
- Increased wildlife crime
- Reduced conservation efforts

Humanitarian Groups

Without Tax Exemption:
- Loss of educational programs
- Negative effects on substance abuse support
- Diminished public trust

Disaster Relief Organizations

Without Tax Exemption:
- Compromised preparedness and training
- Longer recovery times
- Increased inequality in disaster response

Faith-Based Organizations

Without Tax Exemption:
- Loss of community cohesion
- Loss of youth programs
- Closure of smaller congregations

MEDICAL/SCIENTIFIC SOCIETIES, PATIENT ADVOCACY & RESEARCH ORGANIZATIONS
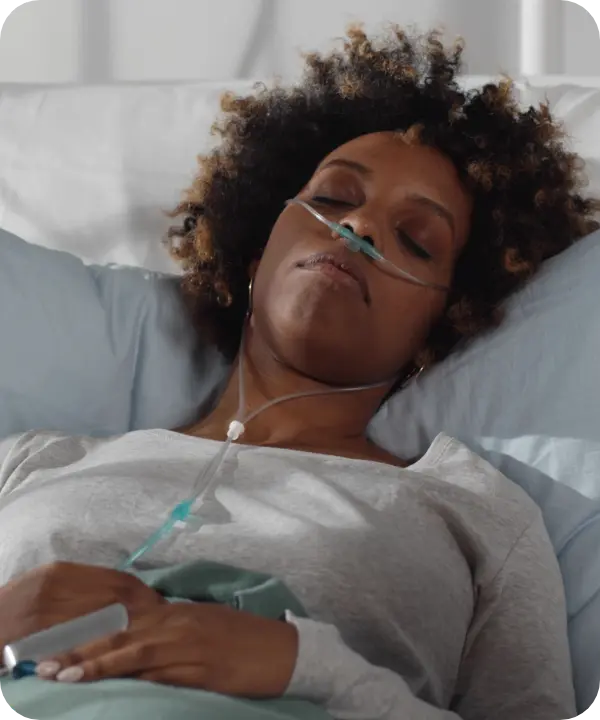
Without Tax Exemption:
- Higher costs for patients
- Slower progress in science and medicine due to limited guidance and support
- Challenges in funding emerging therapies

Poverty & Hunger Relief Groups

Without Tax Exemption:
- Increased homelessness and hunger
- Longer wait times for assistance
- Fewer meals and resources distributed

Veterans Groups

Without Tax Exemption:
- Compromised rehabilitative and housing services
- Restrictions on educational and training programs
- Decreased mental health services

Trade & Professional Associations

Without Tax Exemption:
- Decreased research initiatives
- Difficulty in providing industry standards
- Impact on small businesses

Destination Organizations & Tourism Groups

Without Tax Exemption:
- Reduced investment in local tourism and economic development
- Fewer resources for small businesses and hospitality industries
- Decreased ability to attract events and visitors to America
Affected TAX-EXEMPT ORGANIZATIONS
Download Coalition RESOURCES
Access key resources to support and amplify our mission, including one-pagers, advocacy letters, backgrounders, coalition stories and more.